Summer, beach days & fun in the sun are fast approaching – woohoo! We all know sunscreen is essential to prevent burns, but are the chemicals inside the sunscreen harmful? From sprays to lotions & powders, what’s the safest, cleanest, non-toxic sunscreen? What active ingredient should you look for? How much sun exposure do we really need?
What goes ON your body matters – keep reading for a summer guide on non-toxic sunscreen.

(Note: This article contains affiliate links, meaning In On Around will make a small commission at no additional cost to you. This helps me maintain the site. As always, I value full transparency & only work with brands I love and trust.)
Sunscreen Active Ingredient Safety
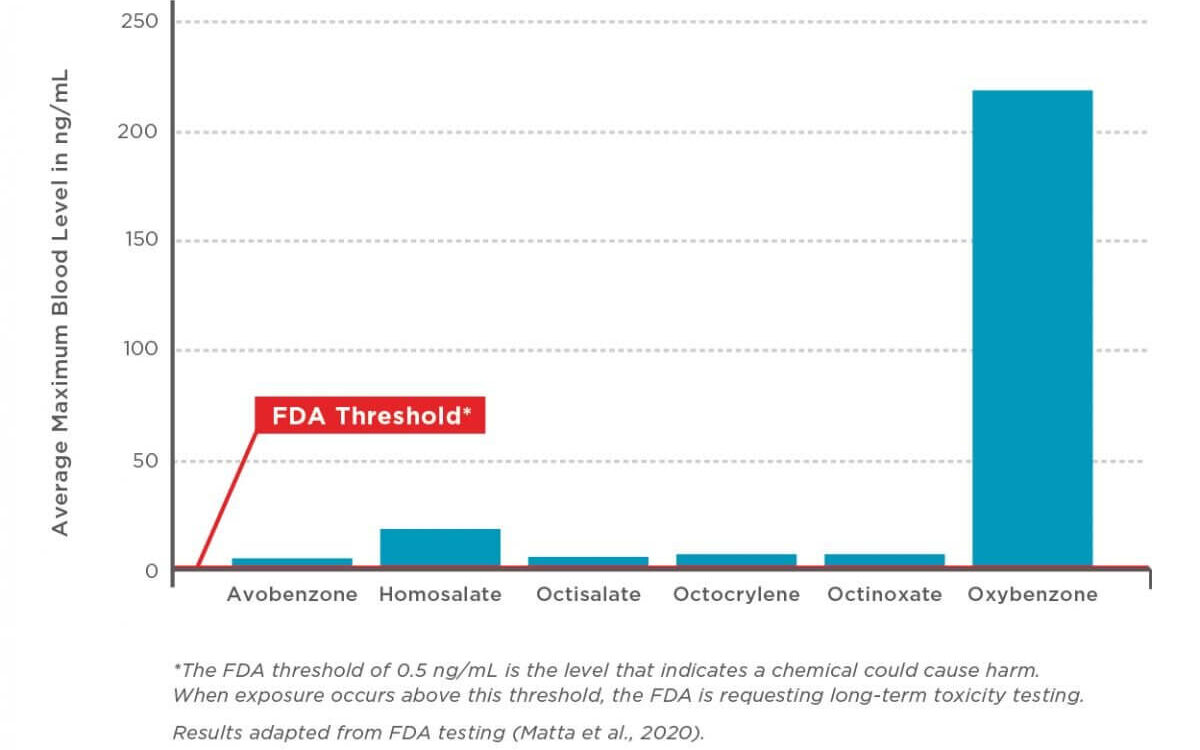
Just last year in 2020, new FDA testing showed that the active ingredients in sunscreen are absorbed into the skin and can stay in the bloodstream for days, sometimes weeks. [1] Even a single application of sunscreen increases the level of the active ingredient in the plasma to above FDA’s threshold – yikes. [2]
Clearly, what used to be considered safe, is being questioned – more quality research is needed. It’s always best to err on the side of caution.
Sunscreen Skin Absorption in FDA Testing:
Information from: EWG
While this data brings into question the safety of specific sunscreen active chemicals, it does not question the importance of sunscreen. Sunscreen is essential to protect our skin from ultraviolet sun rays to protect us from melanoma, skin aging, sunburns, etc…
That being said, it’s important to use the right kind of sunscreen.
How Much Sun Exposure Is Too Much?
A 2016 study shows that while it’s important to prevent skin cancer & to be aware of the sun’s power, the sun isn’t necessarily the enemy. [3] Without adequate sun exposure, it’s common to suffer from Vitamin D deficiencies and other serious health problems.
In fact, some studies have linked low Vitamin D levels to an increased risk of mortality from heart disease and colon cancer, as well as a heightened risk of breast cancer.
The majority of American citizens are Vitamin D deficient.
About 50% of women and men aged 65+ in North America are Vitamin D deficient, as well as 70% of children in the USA. [4, 5] While there’s no specific recommended level of sun exposure, it could be of benefit for the average person to get about 10-30 minutes of midday sunlight exposure every day (also dependant on your skin tone & supplementation amount).
What Is Commonly Found in Sunscreen?
There are many different active ingredients commonly found in sunscreens, such as:
- Oxybenzone
- Octinoxate (Octyl methoxycinnamate)
- Homosalate
- Octisalate
- Octocrylene
- Titanium dioxide
- Zinc oxide
- Avobenzone
- Mexoryl SX
- Retinyl palmitate
… amongst others.
These chemicals either reflect, absorb or scatter the UV rays from the sun. As mentioned, they are absorbed into the body at much, much higher levels than the FDA threshold. Oxybenzone is most commonly used in non-mineral sunscreens and it damages coral reefs. [6] In fact, Hawaii has banned the use of oxybenzone, octinoxate, avobenzone, and octocrylene to protect marine life – this should be a worldwide ban! [7]
Certain states have banned some chemical sunscreen ingredients.
Zinc oxide and titanium dioxide are mineral-based (which is a good thing). They put a product layer over the skin as a “physical sunscreen” or UV blocker.
Oxybenzone, on the other hand, increases the absorption of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (which is a pesticide) by 36.4%, according to this 2004 study. [8] Furthermore, oxybenzone is the most common photoallergen in North America (meaning it can cause allergic reactions due to ultraviolet exposure changing the structure of the drug). [9]
Why is it still being used in sunscreen?! Beats me! Undoubtedly, we need change.
What Should You Look For In Non-toxic Sunscreen?
- Always look for the active ingredients: non-nano zinc oxide
- Nano particles are incredibly small particles that can penetrate the skin. For sunscreens, it’s best to opt for non-nano so the natural ingredients can sit on top of the skin.
- Look for “Broad-Spectrum” SPF – which means it filters out both UVA and UVB rays. It can also be listed as “full spectrum.”
- Be wary of marketing stating “mineral-based” – these can sometimes be mixed with other chemical active ingredients. Make sure to look at the active ingredients list.
Reapply sunscreen often, especially if swimming.
- Avoid conventional sunscreens containing benzophenone, which is an endocrine disruptor, mutagen, and carcinogen (especially common in products containing the SPF ingredient octocylene). [10] Broad spectrum chemical sunscreen ingredients, like benxophenone, can have side effects.
- Avoid sunscreens with other added toxic ingredients, like parabens, phthalates, fragrance… Opt for mineral based brands that are sensitive skin friendly and fragrance free. Organic ingredients are even better! Anything marketed as “water resistant” likely contains PFAS or “forever chemicals.”
- You can learn more about forever chemicals here.
- Instead of opting for sprays or powder, opt for lotion to prevent inhalation.
- Although they’re easy to apply, spray sunscreens can potentially be inhaled. If you must use a spray or powder, make sure you hold your breath as much as possible while applying and walk away from the area.
Note: mineral-based sunscreens can leave a white cast on the skin unless it’s rubbed in thoroughly. Rub in any white residue.
How You Can Internally Protect Against Sun Damage
When our skin is exposed to ultraviolet radiation, we produce “free radicals,” which are unstable particles that can lead to DNA and cell damage. So, what neutralizes these free radicals? Antioxidants are naturally found in many fruits, vegetables, nuts, etc…
Here are the top tips to “eat” your sun protection:
- Eat a plant-based diet rich in healthy fats (high in omega-3s, like milled flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, organic soy)
- Avoid processed foods, added sugars, and inflammatory vegetable oils
- Eat lots of fruits rich in antioxidants (which can prevent free radical damage and skin damage) – apples, berries, beans, dark leafy greens etc…
- Eat fresh fruits & veggies rich in polyphenols, like berries, beans, nuts, organic soy etc… [11]
- Drink your organic green tea & matcha!
- You can find more info on green tea here
- Make sure you’re at an optimal amount of Vitamin D (when your body has enough Vitamin D, it produces melanin, which protects against sun damage)
- Take astaxanthin as a supplement. It has been shown to help protect against UVA-induced skin photo-aging, like sagging. As always, discuss supplementation with your doctor first. [12]
What goes in, on, and around your body matters.
What Are Some Sun Safety & Non-Toxic Sunscreen Best Practice Tips?
- Always put sunscreen on your face & neck to reduce the risk of aging
- In order to ensure adequate production of Vitamin D, stay in the sun for 10-30 minutes before applying non-toxic sunscreen to your body.
- As always, if you’re out in the sun all day, opt for light long-sleeves to cover up as much as possible.
- Stay in the shade as much as possible
- Don’t neglect your scalp! Wearing a large sun hat can protect your head from too much sun exposure. It’s essential not to overlook this part of your body!
- Especially if your skin is fair, stay away from midday sun for long periods of time.
Check Out The In On Around Shop
- Consult with your doctor on your Vitamin D levels – if you’re deficient, especially in the winter months, a high-quality Vitamin D supplement, like Truvani, might be of benefit.
- Those who live in the Northern Hemisphere absorb very little amounts of Vitamin D except during the summer months. Supplements can help ensure you’re within the 800-1,000 IU of Vitamin D per day (no more than 2,000 IU).
- Avoid all sunscreen products with bug spray added
- If you had a little too much fun in the sun and got burnt, fresh aloe to the rescue! Use fresh aloe directly from the plant to help with skin repair. Be careful with many of the packaged aloes, which can oftentimes contain toxic, unnecessary inactive ingredients & preservatives.
- If you’re missing the tan, opt for a natural self-tanner like Beauty By Earth
The Best Non-Toxic Sunscreen Brands
- Favorite Facial Sunscreens:
- Cocokind’s daily SPF, which uses non-nano zinc-oxide. I put it on even if I’m sitting and working at home all day – windows only block out UVB rays, not UVA rays.
- Favorite Body Sunscreens:
- You can find many more sunscreen options in the In On Around Shop (within the Outdoor Protection category). These range from SPF 20, SPF 30, SPF 35, SPF 40, SPF 50, and more. You can find also find the best after-sun aloe vera creams and personal care products in the shop.
Save this sunscreen guide on Pinterest for future reference:

Natural Sunscreen – Frequently Asked Questions
Click on the below FAQs to learn more about sun safety tips, ingredients to avoid, popular sunscreens, titanium dioxide and zinc oxide.
What is the active ingredient in sunscreen?
How can I find a nontoxic sunscreen?
How can you protect your skin from sun damage?
What are the best ways to prevent sunburn?
What kind of sunscreen do you use?
Now it’s time to have some fun in the sun, without harmful chemicals or burns!
Let me know in the comments below! You can watch our web story here.
xoxo,

Want to read more? Check out my other articles here!
Information on sunscreen options and types of sunscreen from: Environmental Working Group, Healthy Children, PubChem, Harvard Health, Cleveland Clinic, Wellness Mama, Healthline, EWG, Solar Works,
Copyright In On Around LLC 2021 © The statements made on this website have not been evaluated by the FDA (U.S. Food & Drug Administration). They are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. The information provided by this website should not be used as individual medical advice and you should always consult your doctor for individual recommendations and treatment.